Just as traditional banks are the infrastructure of the current financial framework, Wanchain believes it’s building a distributed future “bank” .
PROJECT OVERVIEW.
Wanchain is building a distributed future “bank” on the framework of the Ethereum blockchain. Just as traditional banks are the infrastructure of the current financial framework, Wanchain seeks to build a new, distributed infrastructure of digital assets to form an improved and modern framework.
Any blockchain – private, public, or a consortium chain – would be integrated to establish connections between different ledgers and perform low-cost inter ledger asset transfers. In more basic terms, it means Wanchain can allow developers to create financial applications on public chains such as Ethereum and bitcoin, and that any institution or individual can use Wanchain to create their own virtual teller window (effectively, their own bank) to provide services like lending, asset exchange, credit payments, transaction settlements, and other bank-like services.
Smart contracts allow traders to interact across blockchain networks, with privacy protection being offered for all network transactions.
BACKGROUND.
When blockchain technology first reared its head, interoperability was not a subject of much debate; there was only one blockchain and it was all about bitcoin. As time passed, more and more disparate blockchain platforms rose, among them Ethereum, and these various platforms innovated in different directions, creating their own protocols. These protocols make it impossible for the chains to send and receive data from one another for reasons similar to that of why a program designed for Windows OS will not function on Mac OS.
Rather than stifle development and innovation in various sectors, Wanchain proposes to build an external web of connectivity in the form of interoperability protocols or relay systems that allow for differing blockchains to talk to one another. These protocols are designed to both maximize efficiency between disparate blockchain deployments and allow for a co-existence between them to form, creating a more cohesive ecosystem.
HOW IT WORKS.
Wanchain implements cross-chain transfers of assets by setting up connections between the accounts of different blockchains and providing a framework for financial applications based on digital currency and digital assets, as well as implementing a concept-of-privacy.
Wanchain uses smarts contracts to enable transactions without the need for trusted third parties. Let’s say Alice and Bob have accounts on Ethereum and Wanchain respectively, and Alice needs to transfer 10 ETH to Bob. Alice makes a cross-chain transaction request using the Wanchain wallet and initiates a transfer on Ethereum, with the recipient being an Ethereum cross-chain Locked Account.
Wanchain’s validator node receives the cross-chain transaction request, verifies that the transaction has been recorded on Ethereum, and creates a new smart contract token ETH′ (ether prime) on Wanchain, which corresponds to the ETH needing to be cross-transferred to Bob on Wanchain.
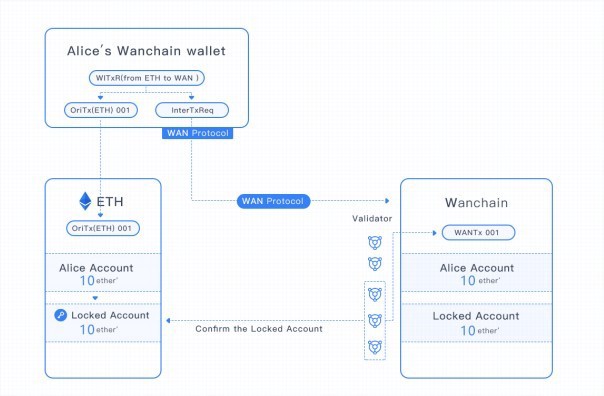 Wanchain’s account locking mechanism and threshold key sharing technology support complete decentralization. This decentralization offers asset account management capability while eliminating the need for the involvement of a third party. A distributed ledger will record both cross-chain and intra-chain transactions.
Wanchain’s account locking mechanism and threshold key sharing technology support complete decentralization. This decentralization offers asset account management capability while eliminating the need for the involvement of a third party. A distributed ledger will record both cross-chain and intra-chain transactions.
INTENDED USE CASES.
Connecting different blockchain networks.
Any blockchain network, whether a public, private or consortium chain, will be able to integrate with Wanchain to establish connections between different blockchains and perform low-cost inter-ledger asset transfers. The asset transfer is achieved through a decentralized cross-chain mechanism and a universal cross-chain protocol. Multiple blockchains will be connected for the purpose of transferring value across networks.
Borrowing and Lending.
A service provider can use a smart contract to create a deposit application and set the interest rate on Wanchain. Through a cross-chain transaction, digital currencies will be transferred from the original chain to a Wanchain smart contract address. A “deposit receipts” in the form of Wanchain tokens will release to the service provider’s account on Wanchain. Interest will be handled by the smart contract too.
On the time of deposit withdrawal, the voucher will be transferred back to an intermediary address, and another cross-chain transaction is executed. The ETH corresponding to the voucher is unlocked on the original chain and transferred back to the original account. Transparency are to be ensured throughout the process.
Payment and Settlement.
Wanchain is a distributed multi-currency platform, integrating different banking ledgers into one unified ledger. Any business or user can install the Wanchain wallet to implement multi-currency payments and settlements without having to install multiple digital currency wallets.
Transaction and Exchange.
As Wanchain will integrate with multiple currencies, multi-currency auction trading and one-to-one curb transactions are possible via smart contracts. Wanchain allows for importing digital currency, launching private transactions and transferring digital currency back to original chain, with privacy protection transaction mechanism such as ring signatures and one-time addresses.
Investment and Financing.
Financial assets recorded in other chains can be linked to Wanchain and investors can use their digital currencies to buy these assets. Moreover, crowdfunding can be done in multi-currency too. For example, an ICO issuer can issue a smart contract that supports multi-currency investments and investors can invest by using Ethereum, Bitcoin or any other blockchain tokens integrated with Wanchain.
Other Applications.
The project team has listed some other use cases such as multiple digital currency credit cards, digital asset backed securities and peer-to-peer lending businesses. Their inter-ledger technologies will also support the future integration of digital assets into banks’ balance sheets.
PROJECT ADVANCEMENTS.
In December 2016, proof of concept development was conducted for token privacy protection of smart contracts. Theoretical proof for token privacy protection of smart contracts based on one-time addresses and ring signatures was completed in 2016, and the POC was completed at the beginning of 2017.
At the beginning of 2017, the design of the cross-chain transaction mechanism and the cryptographic technology was completed.
WANCOIN.
Available once mainnet launches later in the year.
There are transaction fees involved in Wanchain and they are divided by the three categories of verification nodes namely cross-chain transaction proof nodes (Vouchers), locked account management nodes (Storemen) and general verification nodes (Validators).
- A Voucher receive transaction fees for its proof provided but if it is found to be false, the security deposit is deducted from the holding account and the node authority status will be revoked.
- A Validator completes the recording of transactions on Wanchain to gain a part of the transaction fees.
- A Storeman receives a corresponding key share according to the stake it holds, and calculates the corresponding signature share to be added into the transaction. The Storeman obtains the transaction fee involved in the verification transaction according to the key share proportion. If the key share information is offline or lost, the transaction fee cannot be claimed. Likewise, if the nodes sign the error transaction, the credentials of the Storeman will also be taken away.
In summary, the verification node incentive mechanism will motivate the Vouchers to provide correct transaction proof, the Validators to complete the recording of Wanchain faithfully, and the Storemen to stay online and safely keep their own key shares.
Value of coin.
In terms of applications, as more and more cross-chain transactions are run by Wanchain, the more Wancoin rises in value.
COMPETITORS.
 Polkadot.
Polkadot.
Polkadot is a blockchain technology, a heterogeneous multi-chain. It’s a system intended to help various blockchains (including Bitcoin) talk to each other.
It consists of many constituent blockchains, the Para chains, with potentially differing characteristics which can make it easier to achieve anonymity or formal verification. Transactions can be spread out across the chains, allowing many more to be processed in the same period of time. A relay chain coordinates consensus and transaction delivery between chains.
Polkadot ensures that each of these blockchains remains secure and that any dealings between them are faithfully executed. Specialised Para chains called bridges can be created to link independent chains. The Polkadot relay chain creates a relay between multiple “Para-chains”, and is used to take care of the security of the network, thereby creating pooled security for all blockchains within the ecosystem.
The Polkadot ICO has not been announced yet.
Cosmos.
Cosmos is a network and a framework for interoperability between blockchains. The Cosmos proof-of-stake-based blockchain consists of many independent, parallel blockchains, which are connected to each other with the help of a Cosmos Hub. Cosmos’ plan to function as a relay between various deployments of a blockchain is similar to a translator between individuals who speak different languages.
Cosmos Fundraiser raised $17 million in half an hour
KyberNetwork.
Another project hinging upon interoperability protocols is the KyberNetwork, founded by Loi Luu. Luu built the KyberNetwork to allow transactions between paying parties and recipients who don’t have access to the same digital currency. Interoperability protocols will grant incompatible blockchains the means to form a viable ecosystem.
Smart contracts ensure that the transactions are secure and trustless. The execution of conversion is decentralized and it is instantaneous. The platform also provides APIs for payment that ensures that a merchant will receive the payments in Ether irrespective of the token that was used by the customer to make the payment.
Kyber Network manages to make conversions and trading instantaneous because they hold a reserve warehouse with the appropriate amount of various cryptocurrencies. A Kyber contract controls the reserve. The platform has been designed to allow new coins to be added in the future.
Unlike Kyber which claims it will reward reserves, Wanchain lacks Influencers.
Trading at $$1.72 since its March, 2017 opening at a price of 1.85.
Ripple.
Ripple connects banks, payment providers, digital asset exchanges and corporates via Ripple Net to provide one frictionless experience to send money globally. Ripple, has since its creation, been adopted by a greater number of banks. The intention of Ripple is to reduce the transaction fees, processing delays (an estimated 70,000 transactions can be performed in under a second) and provide a blockchain (a public ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions that have ever been performed and can be viewed by anyone at any time to see the transactions and their validations). However, with Ripple owning 61% of all the XRP (XRP = Ripple ticker symbol), it can be argued that the system is more-so centralized.
Ark.
ARK provides users, developers, and startups with innovative blockchain technologies. Accessible via push button clone-able blockchains, and our SmartBridge technology. ARK aims to create an entire ecosystem of linked chains and a virtual spiderweb of endless use-cases that make ARK highly flexible, adaptable, and scalable. ARK is a secure platform designed for mass adoption and will deliver the services that consumers want and developers need.
Trading at $2.74 since its March, 2017 opening at a price of 0.032677.
Shapeshift.
Offers exchange just like Shapeshift, but offers the smart contract system.
This is a decentralized bank. However, Polybius is not using its platform for communications/exchanges/privacy protection between other ledgers but exclusively and native to the Ethereum ledger. Polybius is built on the Ethereum network and is working exclusively within this platform. Wanchain is built on Ethereum but will create smart contracts not only within Ethereum blockchain as a decentralized bank but between other blockchains as well.
Trading at $4.46 since its July, 2017 opening at a price of 8.35.
Bankera.
Bankera is building a digital bank to last for the blockchain era. As a traditional bank, Bankera’s services fit into three groups:
Payments including payment accounts with personal IBAN, debit cards, interbank foreign exchange rates and payment processing. All services will support both traditional fiat currencies as well as cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, DASH, NEM, ERC20 compliant tokens and others. In the long term, Bankera will implement innovative solutions such as gross-domestic-product (GDP) linked currencies and the use of equity traded funds as a substitute for money.
Loans and deposits will be a key competitive edge as well as core service of Bankera. Current deposits will receive interest just as savings do. All Bankera clients will be able to benefit from higher interest rates due to proprietary information about borrowers’ cash flow, as most loans will be given to business clients who use the payment processing solution.
Investments will consist of low-cost investment products such as equity traded funds (ETFs), crypto-funds (a portfolio of various cryptocurrencies and crypto tokens) as well as roboadvisory solutions for wealth management. Eventually, Bankera will offer investment banking services including financing corporate strategies of our business clients.
Bankera will function more in a centralized way. It is completely different to Wanchain that aims at being a decentralized and distributed financial market - offering concept-of-privacy (privacy protection of users) as well as incorporating secure transactions between other blockchains.
Blocknet.
Another project is Blocknet,a DApp platform. Blocknet is a revolutionary advancement in cryptographic technology: a true peer-to-peer protocol between nodes on different blockchains. This is the foundation of a technology stack incorporating an API and an application platform, which enables open-ended application possibilities and vastly reduces development time.
Trading at $23.86 since its Nov 2014 opening at a price of 0.079314.
What’s the difference between Wanchain and its competitos?
Wanchain achieves the privacy protection of smart contract token transactions using ring signatures and one-time addresses. As the Wanchain.org official website explains, this makes Wanchain the first to achieve privacy protection for smart contract token transactions. This is a key development that will make Wanchain and blockchains more applicable to financial applications.






















